In a world where we navigate the digital realm daily, the security of our online activities has never been more critical. Imagine typing in a website’s address, expecting to reach a legitimate destination, only to be redirected to a malicious site. This unsettling scenario is precisely what DNS spoofing, a cunning cyber threat, brings to the table. In this article, we’ll journey into the fascinating yet concerning world of DNS spoofing. We’ll unravel what it is, how it works, and most importantly, how to protect yourself from this potentially dangerous threat. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned pro, understanding DNS spoofing is essential for safeguarding your digital adventures.
What is DNS Spoofing?
Before we delve into the depths of DNS spoofing, let’s grasp the fundamentals. DNS, or Domain Name System, is the internet’s phonebook. It translates user-friendly domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers understand. When you enter a web address into your browser, the DNS server provides the correct IP address, allowing your device to connect to the desired website.
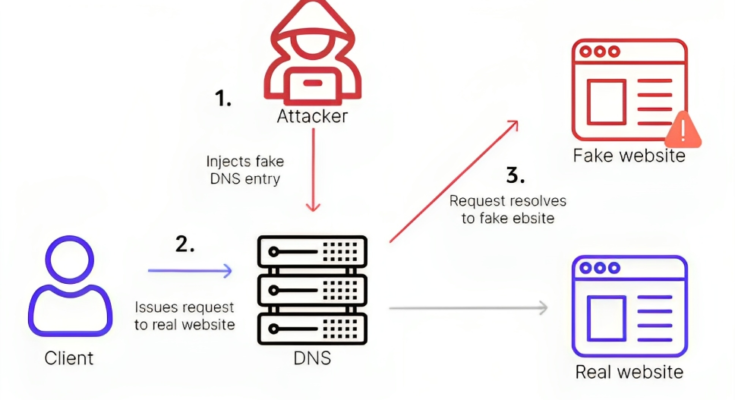
DNS spoofing, also known as DNS cache poisoning, is a deceitful technique cybercriminals employ. It involves corrupting the DNS server’s cache with fraudulent IP address entries and redirecting users to malicious websites without their knowledge or consent. This kind of rerouting can have dire consequences, from exposing sensitive data to spreading malware.
How DNS Spoofing Works
1. Vulnerabilities in the DNS
DNS spoofing takes advantage of vulnerabilities within the DNS system. These vulnerabilities can be present in DNS software, configuration settings, or even in the communication between DNS servers.
2. Intercepting DNS Requests
When a user enters a web address, their device sends a DNS request to the DNS server, asking for the IP address associated with the domain. An attacker intercepts this request and sends a forged reply to the user, providing the IP address of a malicious site instead.
3. Caching the Fake Data
The user’s device stores this fraudulent IP address in its DNS cache. Subsequent requests to access the same website are then rerouted to the attacker’s malicious server rather than the legitimate destination.
4. The Deceptive Outcome
To the user, everything appears normal. They land on a legitimate website, unaware that they’ve fallen into the attacker’s trap. This can lead to the exposure of sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
The Potential Dangers
1. Phishing Attacks
DNS spoofing is a potent tool for cybercriminals to conduct phishing attacks. Users believe they are on a legitimate website, making it easier for attackers to steal sensitive data like login credentials or personal information.
2. Malware Distribution
By redirecting users to malicious sites, attackers can easily distribute malware. Users who unknowingly download malware can infect their devices, leading to data loss or system compromise.
3. Data Theft
Sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, social security information, or confidential business data, can be stolen when users are rerouted to fake websites designed to capture this information.
4. Identity Theft
Attackers can use DNS spoofing to impersonate legitimate organizations, leading to identity theft. Users who provide personal information on these fake sites become vulnerable to identity theft.
Protecting Yourself from DNS Spoofing
1. Use Secure DNS Servers
Opt for secure and reputable DNS servers, such as those provided by your internet service provider (ISP) or well-known third-party DNS providers. Secure DNS servers implement additional security measures to protect against spoofing.
2. Enable DNSSEC
DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is a technology that adds a layer of security to the DNS. When DNSSEC is enabled, it verifies the authenticity of DNS responses, helping to prevent spoofing.
3. Keep Software Updated
Regularly update your DNS software and other critical system components. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities.
4. Employ a VPN
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can add an extra layer of protection. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept your DNS requests.
5. Be Wary of Suspicious Links
Practice caution when clicking on links in emails or on websites. Verify the legitimacy of a website before entering sensitive information. Look for signs of secure websites, such as “https://” and a padlock icon in the address bar.
Summary
In an era where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the digital realm, DNS spoofing poses a genuine threat to our cybersecurity. It’s not just about protecting your data; it’s also about safeguarding your identity and online presence. By understanding how DNS spoofing works and taking proactive steps to protect yourself, you can navigate the internet with greater confidence and security.
As technology evolves, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. Staying informed and implementing best practices is your best defense against the potentially dangerous world of DNS spoofing. Stay vigilant, keep your digital guard up, and you’ll be better prepared to thwart the deceptive intentions of those who seek to exploit your online presence.