In today’s data-driven world, where information is the lifeblood of businesses and organizations, the choice of how to store and manage data is of paramount importance. Two giants have emerged in this arena: traditional databases and blockchain technology. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, but understanding the differences between them is essential for making informed decisions about data management.
This article will compare blockchain and traditional databases. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of which solution might be right for your needs.
The Essence of Traditional Databases
At Its Core: Traditional databases, like those based on SQL (Structured Query Language), have been the backbone of data management for decades. They are centralized repositories where data is stored in tables with rows and columns.
The Structure: Think of a traditional database as a well-organized digital filing cabinet. Data is neatly arranged in rows (records) and columns (attributes), making it easy to retrieve and manipulate.
The Rise of Blockchain
Blockchain is a relative newcomer, gaining fame primarily through cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It’s a decentralized, distributed ledger technology where data is stored in a chain of blocks, each containing a set of transactions.
In a blockchain, data is linked together in chronological order. Each block references the previous one, forming an immutable chain. This structure ensures transparency and security.
The Showdown: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Let’s dive into the details and compare these two systems in the data management arena:
1. Centralization vs. Decentralization
Centralized Databases: Traditional databases are centralized. They are managed by a single entity or organization with full control over the data.
Blockchain: Blockchain is decentralized. Data is stored across a network of computers (nodes), with no single entity having complete control. This enhances security and reduces the risk of manipulation.
2. Data Structure
Centralized Databases: Data in traditional databases is structured and organized, making it suitable for complex queries and reporting.
Blockchain: Data in a blockchain is less structured and is often used for simple transactions. Complex querying can be challenging.
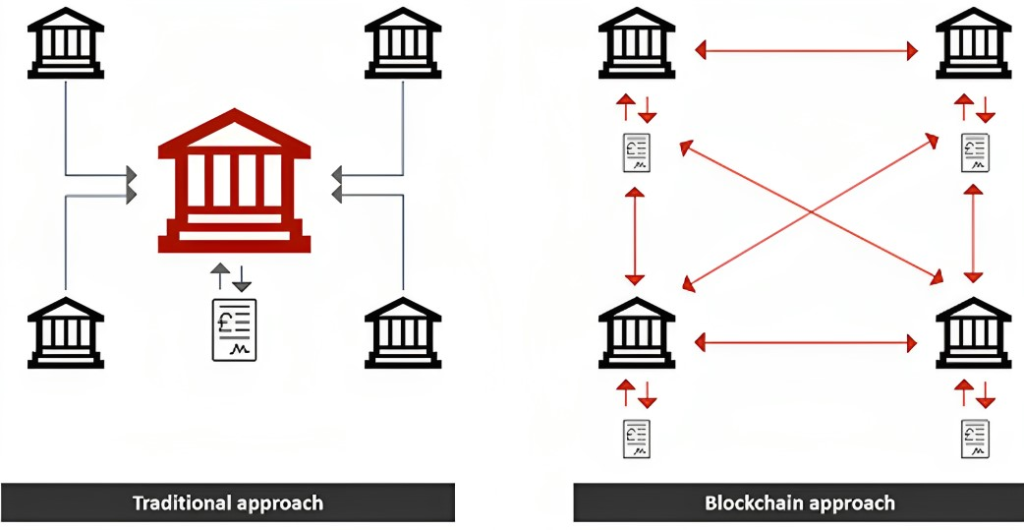
3. Transparency and Immutability
Centralized Databases: Traditional databases can be altered or manipulated by those with access. They lack the transparency and immutability of blockchain.
Blockchain: Data on a blockchain is transparent and immutable. Once a record is added, it can’t be changed or deleted, ensuring trust and data integrity.
4. Security
Centralized Databases: Security relies on the measures put in place by the central authority. Vulnerabilities can be exploited if not adequately protected.
Blockchain: Blockchain is highly secure due to its cryptographic nature and decentralized structure. Hacking a blockchain is extremely difficult.
5. Use Cases
Centralized Databases: Traditional databases excel in scenarios where complex queries, reporting, and structured data are essential, such as banking and finance.
Blockchain: Blockchain shines in situations where transparency, security, and trust are paramount, like supply chain tracking and cryptocurrency transactions.
The Future of Data Management
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of data management, the choice between traditional databases and blockchain will depend on specific needs and objectives. While traditional databases continue to be the go-to choice for many applications, blockchain’s decentralized and secure nature is opening doors to innovative solutions across industries.
In conclusion, the battle between traditional databases and blockchain is not a clear-cut winner-takes-all scenario. Instead, it’s a matter of selecting the right tool for the job. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each, you can make informed decisions that align with your data management goals. Whether you opt for the familiarity of a traditional database or the revolutionary potential of blockchain, one thing is certain: the world of data management is continually evolving, and staying informed is key to success.